Though pelvic pressure, abdominal swelling and pelvic pain are the most common symptoms of ovarian cancer, there does seem to be a connection between ovarian cancer and leg pain. Scroll down to find out why women suffering from this serious medical condition may experience leg pain.
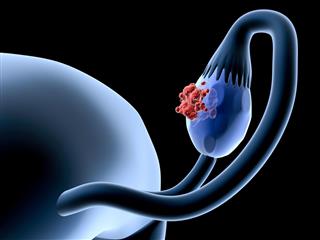
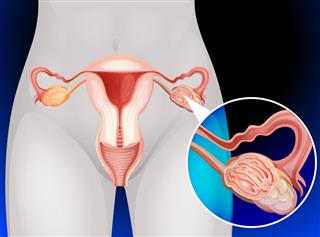
Ovaries are oval-shaped paired glands that are located on either side of the uterus in the pelvic cavity. Ovaries are gonads or sex glands wherein the sex cells are produced. These are a vital part of the female reproductive system. Ovaries are ovum-producing glands that are analogous to testes, which in turn, are sperm-producing glands in males. Since ovaries produce certain hormones, these are a part of the endocrine system in women.
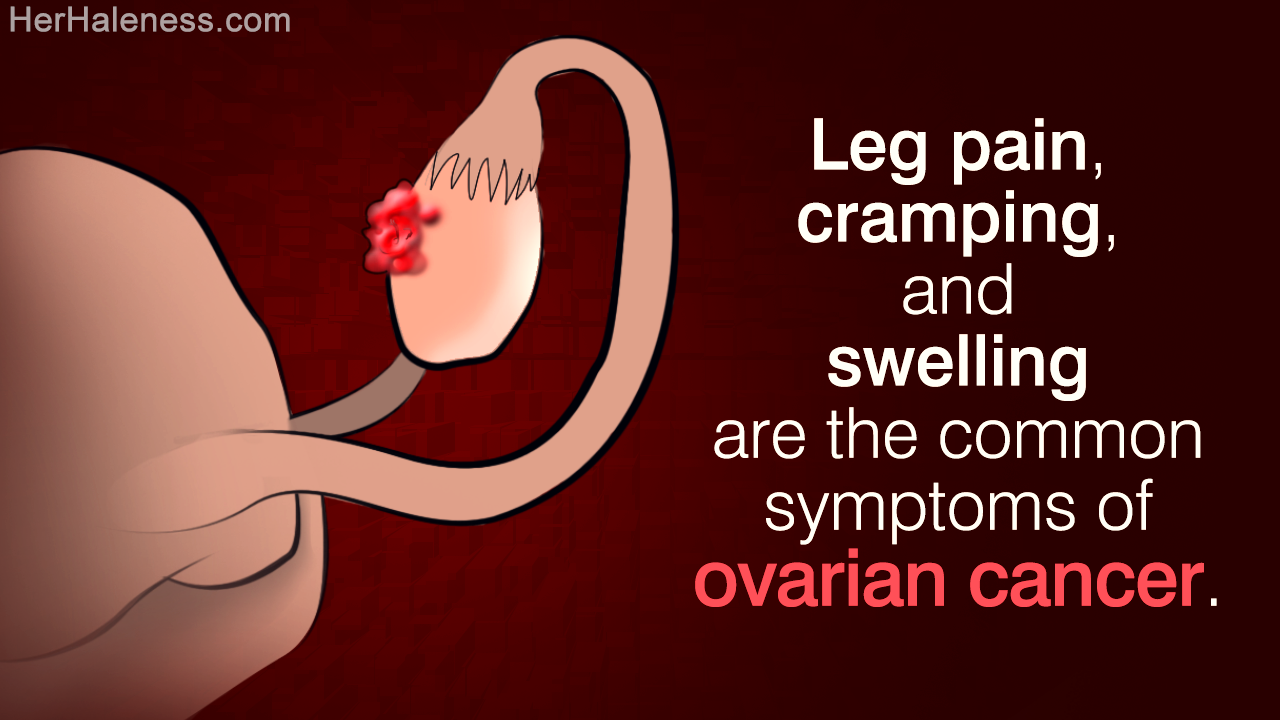
Ovarian cancer, as the name suggests, occurs when an uncontrollable and abnormal cell division leads to the development of a malignant growth in one or both ovaries. The symptoms may not be noticeable in the initial stages, but as the disease progresses, women may experience leg pain, leg cramps, abdominal cramping, swelling in lower extremities, pelvic pressure, urinary problems or pain in the pelvic region. In this article, we will look into the connection between ovarian cancer and leg pain.
Can Ovarian Cancer Cause Leg Pain?
As mentioned earlier, leg pain, cramping, and swelling are some of the most common warning signs of ovarian cancer. While abdominal swelling is one of the most common symptoms of ovarian cancer, usually the pain from the cancerous growth radiates to the lower back, from where it may radiate to the legs. The pain that is experienced in the thighs and lower extremities is basically a referred pain. Though pain may originate in the pelvic region, it is felt in areas other than the place of origin. The proximity of the female reproductive organs to the legs is the main contributing factor.
Since the ovaries are located near the pelvic bones, benign as well as cancerous growth can impinge on the nerves that supply sensation to the legs. Under such circumstances, there is a great likelihood of the patient suffering from frequent bouts of leg pain. This may also explain the link between ovarian cancer and leg cramps. Women suffering from ovarian cancer often complain about swelling in legs. Well, leg swelling may occur if the veins that carry fluid from the legs to the heart get constricted. If the cancerous growth enlarges and starts pressing against these veins, the veins may become narrow and fluid may accumulate in the legs. Besides pelvic pain and leg pain, women suffering from ovarian cancer may also experience symptoms such as constipation, bloating, indigestion, pain during intercourse, urinary problems, menstrual irregularities, and vaginal discharge.
Treatment of Ovarian Cancer
Women who have a family history of ovarian cancer must consult a gynecologist if they ever experience aforementioned symptoms. In the first and second stages, the cancerous cells stay within the pelvic region, but in the third and fourth stages, cancer may spread to other parts of the body. There is a great need to slow down the progression of this disease. Ovarian cancer has the reputation of being a ‘silent killer’. The symptoms start making an appearance later and if this condition is detected in the advanced stage, it can have serious repercussions on one’s health.
A persistent pelvic pain, leg pain, and other common symptoms must, therefore, never be taken casually. Treating ovarian cancer would naturally help in treating leg pain and all the aforementioned symptoms. If detected early, surgery can help in controlling cancer.
Surgical procedures that are used for the treatment of ovarian cancer include a total hysterectomy. This procedure involves the removal of the entire uterus. Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy refers to the removal of both the fallopian tubes as well as the ovaries. Surgeons may also consider the total or partial removal of the fatty layer that envelops the organs in the abdominal cavity. The decision regarding the most suitable surgical procedure in each case is usually made after taking the age of the patient into consideration along with the extent to which cancer has spread.
If cancer is detected at an early stage and the patient wishes to conceive in future, then doctors may not remove the entire uterus and would consider the removal of just the affected ovary or fallopian tube. After the surgery, other treatment options would be recommended. For instance, the patient would have to take anticancer drugs or chemical agents for killing the cancerous cells. This is referred to as chemotherapy. Radiotherapy is another method that is not as commonly used as chemotherapy. Under this procedure, high energy rays are directed at the cancerous cells so as to destroy them.
Leg pain, pelvic pain, and swelling in the abdominal region are some of the warning signs of ovarian cancer. So, if you ever experience symptoms associated with ovarian cancer, get a thorough medical checkup done at the earliest. The success rate of ovarian surgery is high, especially when cancerous growth is detected at an early stage.
Disclaimer: This article is for informative purposes only, and should not be used as a replacement for expert medical advice.